What is safety?
Protecting yourself and others
Safety is the absence of injury,
Procedures intended to prevent injury
Freedom from danger, risk, or injury


Safety awareness
Safety awareness is a most important precaution to stay away you from hurting or killing someone else
To create a safe workplace
Clean work area
Tools would be clean
Proper tools for opening /closing
All equipment safety guards installed
Equipment and power tools properly grounded
Safety Plan
A Safety Plan is a written document that describes the process for identifying the physical and health hazards that could harm workers, procedures to prevent accidents, and steps to take when accidents occur. Written safety plans can be comprehensive, such as an injury and illness prevention program, or they can be specific to a particular activity, hazard, or piece of equipment. The written safety plan is your blueprint for keeping workers safe. Many organizations compile their activity-specific safety plans into a single safety manual.
However, Our Company is committed to providing the safest possible working environment and conditions for our Employees. The safety of our employees is a prime concern to management. With this in mind the following management commitment is being made to prevent unnecessary injuries to our employees.
The prevention of employee injuries is of the utmost importance and a key ingredient to the continued success and growth of our company. We urge each of you to join with us in committing to make our company the safest possible place to work.
Each employee has a personal responsibility to work safely. In a broad sense all employees are members of the safety committee. All employees, together, have the responsibility to create and maintain a workplace that is free of unsafe and hazardous work assignments. Your second responsibility is to use only safe procedures in your work. Also, when you see an unsafe or possibly unsafe condition in the workplace, or when you see what is or possibly may be unsafe work behavior, you are to correct it if possible. And you are to report it to your supervisor.
This is important so that management can make necessary decisions to improve safe working conditions and safe working behaviors.
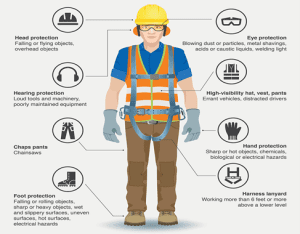
Personal Protective Equipment’s
Safety Helmet
Safety Glasses/Face Shields
Hearing protection
Hand Gloves
Visible Vest
Steel Toe Boots
Respirators/Dust Masks
Our workplace has an active safety program. Your first responsibility is to learn safe procedures for performing your
Toolbox Talk

Toolbox talks are a useful tool in the maintenance of a viable safety and health education program in the any construction industry.
Schedule a daily morning meeting before stare any activities with all the engineers and workers to understand the activities and also associate risk.
Keep an attendance sheet with sign to make sure everyone is attained, if someone miss let know them the tool box talk summary.
Allow us and our workers to explore the risks of specific health and safety issues and think about ways to deal with them.
Encourage worker engagement.
Help support a planned series of site observations.
Encourage health and safety to become everyone’s responsibility.
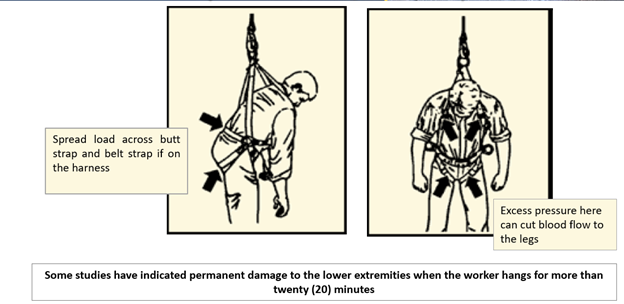
Work at Hight
Any work to be performed at a height of 1.8 meters or above from the ground level where a person is standing is defined as work at height. Even a job being carried out below the ground level is classified as work at height. (Eg: Work in an excavated area is a work at height). For jobs at more than 1.8 mtr. height, where there is no permanent platform, the job requires a permit to work along with a work at height checklist.
Without Use of PPE’s
Without use Fall protection systems
Slippery Surface
Damaged Platform & Railing
Improper use of staircase
Poor Scaffolding condition
Lack of knowledge about work at height procedure
Poor Health condition & Acrophobia
Poor House keeping
Before start a job on scaffold. Must be check scaffold condition and check list.
Keep Access and egress way are clean and neat
Keep three-point contact on Ladder
Must be use proper tools and equipment’s
Must be use Proper PPE’s,
Must Be use Proper Fall Protection System
Only Work trained and Knowledgeable person
Barricade the work at height area
Maintain Good Housekeeping on Platform
All the person should be known about the rescue plan
Report Near Misses

Hot Work
Hot work any work that may generate a source of ignition like as welding, cutting, grinding and use of torches in areas that are not designed for such activity. Hot work accounts for a significant number of serious fires in business and industry every year due to the hot work causing accidental fire. A Hot Work procedure minimizes the chance that such a fire will occur in our facility.
Performing hot work in areas that are not designed for operation of flame- or spark-producing equipment can cause an accidental fire because of:
Flame contact with combustible material
Sparks settling in combustible material, often falling through a hole in the floor or wall
Heat transmitted through pipes, ducts or conduit to a remote combustible material
Ignition of flammable vapor or dust in the air
All fixed fire protection systems must be in operation
A Hot Work Permit must be completed and a trained fire watch assigned
All flammable and combustible material must be kept at least 35 feet away from the job area. You may also have to use a meter to check flammable gas, vapor or dust levels.
Combustible material that cannot be moved must be protected with fire proof tarps or shields
Wall and floor openings must be plugged with fire proof material
Use shields to protect others from weld flash
Enclosed equipment that contained flammable or combustible material must be cleaned and purged
If necessary, a Confined Space Entry Permit must be secured
A Hot Work Permit must be completed and signed for all work involving: welding, cutting, grinding, soldering, brazing and use of torches or flames
The Hot Work Permit must be signed by your supervisor after necessary precautions are taken
The Hot Work Permit must be displayed at the job site until job completion
A fire watch must be at the job site until one-half hour after the job completion
Expired Hot Work Permits are retained for facility records
Definition: A fire watch is a worker trained and assigned to stay in the area of hot work and look for any evidence of an accidental fire.
Duties:
Have fire extinguishing equipment available for immediate use and be prepared to turn in a fire alarm
Watch for any hazardous conditions and stop the hot work in the event of any potential fire hazard development
Continually check all areas where a fire could start including: the floor below and floor above and the opposite side of walls and petitions
Keep all fire proof tarps and shields in place
Remain in constant attendance (including breaks and lunch) until 30 minutes after the job is complete
Electrical Work
Only trained maintenance employees are authorized to conduct trouble shooting or electrical repairs.
Do not attempt any maintenance activities you are not trained or authorized to conduct.
Never use a damaged extension cord or any other piece of damaged equipment.
Never used electrical equipment in damp or wet areas.
Electrical Shock
Electrical Explosions
Electrical Burns
This can result in severe injury or death.
Before Starting Work
Disconnect from all electrical energy
De-energize all the power sources
Lock & Tag All Sources
- Place Lock and Tag on each of the isolation Barkers
- Attached lock so to prevent operating the disconnecting means.
- Place tag with each lock
If a Lock cannot be applied
- Remove other mean of isolation circuit elements like as fuse
- Blocking of a controlling switch
- Opening of an extra disconnecting device
Release Stored Energy
- Short-circuit and grounding all high capacitance elements
- Discharge all capacitors
Conduct test and visual inspection to ensure all tools, electrical jumpers, short, grounds, and other such devices have been removed
Properly check all the connections with Multimeter whether it is short circuited or not.
Warn Everybody to say out from the electrical panels or equipment’s.
Each lock and tag should remove by the authorized person who applied it.
Visually check that everyone is in a safe distance.
Keep all the fire extinguishing equipment’s neared to work place.
Use post sign and barricades (if necessary, use attendance)
Always use insulated tools and rubber mats to energizing power.
Lifting and Moving Materials
Handling Materials manually
- Lifting by person
Using moving machinery like
- Fork Lift Trucks
- Mobile Cranes
- Overhead and Gantry Cranes etc.
Poor site layouts
Falls from Vehicle
Height Restriction
Overturning
Collisions
Striking people and equipment
Who should use?
- Trained Drivers and Operators
- Adequately skilled
- No persons below 18 years of age
- All lifting machines and lifting tackles bearing
⇒ Identification mark
⇒ Safe Working Load
⇒ Date of Last test
General Precautions
- The Load is safe and secured while lifting
- Slinging method is proper
- Lifted load not exceeding safe working load
- Load is so slung, that it will not collapse or does not damage the sling
- No load is unattended when power is on or load is suspended above machinery
- No person shall ride on the suspended load or lifting machinery
- All persons shall strictly use helmets and safety shoes
Tools and Equipment
Every tool was designed to do a certain job; use it only for the intended purpose.
Don’t force tools beyond their capacity or use “cheaters” to increase their capacity.
All portable electric tools must be grounded’
All damaged cords, plugs, or switches must be immediately taken out of service and returned to the shop for repair.
All pneumatic hose connections must be fastened securely with wire or pins.
Ensure that all side handles are in place on hammer drills. Utilizing the side handle will increase leverage in the event that the bit gets stuck.
Only employees who possess valid credentials are permitted to use powder-actuated tools.
House Keeping
Housekeeping is the foundation of a good safety program.
Keep your work area clean. A clean work area is a safe area.
Remove or bend over all protruding nails, staples, or screws that present a hazard to employees.
Dispose of or clean up spilled material, scrap, and other tripping hazards out of walkways, stairs, and away from emergency equipment.
Cover all exposed re-bar ends that pose an impalement hazard with appropriate protection, such as re-bar caps, lumber in combination with yellow caps, and wooden troughs.
Emergency Evacuation
If there is an emergency:
Proceed to the nearest EXIT. Do not stop to pick up personal property.
After exiting workplace, proceed to the assigned outside Evacuation Area.
The Emergency Coordinator will verify all employees are accounted for.
The Emergency Coordinator will notify the Manager on the status of employees.

Injuries & Accidents
All injuries and accidents must be reported to the manager immediately.
This includes first aid injuries and close calls.
Accidents and injuries resulting in medical treatment must be documented on an accident investigation form.
Prohibited Activities at Project Site
Consumption of Alcohol, Smoking and Drugs items are strictly prohibited in project site at all times regardless of someone in working hours or not.
No one permitted to carry or bringing Gun and other sharp to the project site.